Kali Linux Basic Commands
Kali Linux command is a powerful penetration testing distribution by offensive security. It is available in 32-bit, 64-bit and ARM flavors. With the help of the Kali Linux features, we can easily create custom complex images. Kali Linux offers various certifications such as OSCP, OSWE, OSEP, OSWP, OSEE, and KLCP. The testing tools of the Kali Linux commands can be categorized into information gathering, password attacks, vulnerability assessment, web applications, exploitation tools, sniffing and spoofing, maintaining access, system services and reporting tools.
Kali Linux comprises various tools that can be used for wireless attacks, hardware hacking, forensics, stress testing, and reverse engineering. A USB disk, hard disk, or Live DVD can be used to install it. Network services are HTTP, MYSQL, and SSH. These are quite useful when using the Kali Linux commands.
Kali Linux operates on some android devices. Its predecessor is Backtrack which was carried over to Kali via Live Boot. The system becomes easy to use once the users get the command over it.
The following is the list of Kali Linux basic commands:
Date Command
Cal Command
Cd command
Cp command
Whoami Command
Ls command
cat command
mkdir command
rm command
mv command
Uname command
Uptime command
Users Command
Less command
More command
Vi Command
Free Command
Sort Command
History Command
Pwd Command
1. Date Command
In Kali Linux, the 'date' command is used to display the system date and time. In order to display the date, we have to use the following command:
Syntax:
# date
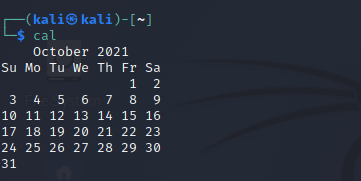
2. Cal Command
The cal command displays the current month's formatted calendar on our terminal screen. If we require a more advanced version of cal, we can install the ncal package on our Linux machine, which displays the calendar vertically and provides additional options.
Syntax
# Cal
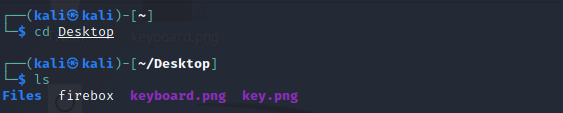
3. Cd Command
The 'cd' command is also called chdir (Change Directory). We used this command to change or switch the current working directory.
4. cp Command
In Kali Linux, the 'cp' command is used to copy files or a group of files or directories that create an exact image of a file on a disk with a different file name.
5. whoami Command
The 'whoami' command is used to print the effective user ID whereas the who command prints information regarding users who are presently logged in.
The "w" command can also be used to view who is logged on and what they are doing.
6. Ls Command
ADVERTISEMENT
One of the most useful commands in Kali Linux is the 'ls' command. The ls command lists the directory contents of files and directories. With the help of the ls command, we can easily list out every hidden file of a directory with the -a attribute, and for more detailed output, we can use the -l attribute.
Syntax
# ls -al
7. Cat Command
The 'cat' (concatenate) command is one of Kali Linux's most commonly used commands, permitting us to create single or many files, concatenate files and redirect, view contain of file output in terminal or files.
Usually, we use the cat command to display the content of a file.
Syntax
# cat filename
Kali Linux Basic Commands
8. mkdir Command
The 'mkdir' command is used to create directories. For example, if we wish to create a directory named 'Penetration testing' under the 'Documents' directory, then we have to open a terminal and enter the below command:
cd Documents
mkdir Penetration testing
ls
9. rm Command
In Kali Linux, the 'rm' command is used to delete files. It can be used to delete directories when we use them recursively.
The removal process separates a file name form its associated data in a file system and identifies that space in the storage device as available for future writes. In other words, when we erase a file. the data inside it remains unchanged, but it is no longer linked to a filename.
10. mv Command
With the help of the 'mv' command, we can move or renames files and directories on our file system.
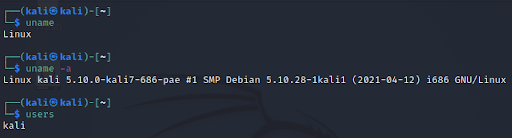
11. uname Command
The 'uname' command displays the current system's information. We can view system information about our Linux environment with the uname command in Linux. With the uname -a command, we can learn more about our system, including Kernel Name, Node Name, Kernel Release, Kernel Version, Hardware Platform, Processor, and Operating System.
Syntax
# uname
12. uptime Command
The 'uptime' command displays the amount of time the system has been running. Uptime's basic usage is simple: simply type the name of the command and click Enter.
Use the -p command-line option if we merely want to know how long the system has been up for and in a more human-readable format.
Syntax
# uptime
13. users Command
The 'users' command is used to display the login names of users logged in on the system.
Syntax
# users
14. less Command
In Kali Linux, the 'less' command is used to view files instead of opening the file. The less command is a more powerful variant of the "more" command which is used to show information one page at a time to the terminal.
We can view any text file with the help of the "less" command simply by typing the following command into a terminal window:
Syntax:
# less /etc/passwd
15. more Command
The "more" command permits us to show output in the terminal one page at a time. This is particularly beneficial when using a command that requires a lot of scrolling, such as the 'ls' command or the 'du' commands.
The 'more' command works with any applications that output to the screen. A good way to test this is to type the following command into a terminal window:
Syntax:
# more/etc/passwd
16. vi Command
The 'vi' editor is a screen editor that comes with practically every UNIX system. The command mode and the insert mode are the two most common nodes in vi.
In order to start entering text in an empty file, we have to first switch from the command mode to the insert mode. To accomplish this, start typing the letter i. When we start typing, anything then the type will be entered into the file.
Type some short lines, then press Return at the end of each. Vi does not use word wrap like other word processors. It will break a line at the screen' edge. If we make a mistake, we can undo it by pressing the Backspace key. If the Backspace key on our computer is not working, then try the ctrl + h key combination.
17. free Command
In Kali Linux, the 'free' command provides us the useful information about the amount of RAM available on a Linux machine. It also displays the entire amount of physical memory used and available space, as well as swap memory with kernel buffers.
Syntax:
# free
If we use the free command with the -t option, it would list the total line at the end.
18. sort Command
Using the 'sort' command, we can sort the content of the text file, line by line. Sort is a standard command-line program which prints the lines of its input or concentration of all files listed in its argument list in sorted order.
Syntax:
# sort file name
We can reverse the order of any file's contents by using the -r sort.
Syntax:
# sort -r
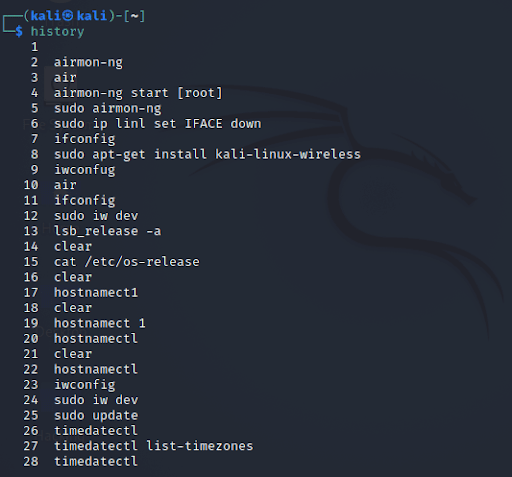
19. history Command
The 'history' command is one of Kali Linux's most commonly used commands. The history command in the bash shell saves a history of commands entered that can be used to repeat commands.
We can run the history command by itself, and it will just print the current user's bash history on the screen, as shown below:
Syntax:
# history
20. Pwd Command
In Kali Linux, the 'Pwd' command is used to print working directory. It gives us information about the directory we are now in. This is especially useful if we need to access the directory while in the middle of a complicated process.
Syntax:
# pwd




















![AIRAVAT RAT FULL SETUP [Android]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg7d-Y8VZygPQPkWhz3nqhDBNSw7SsFr6eBrTu9cNeDNlu7uLXl22ex8uXs4FMo0_N7YYPJLVVsFGbxtztdwOvB0oGEW0ZwftHE_oJl0jusLSLTfSc3qLsR8VbpyhnmxpAF2nEXwtEN91-bP4-H31jbsgnETs09pWzyqDXfelwpa1H0fG5VRa4CaiAMUkqG/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/download-removebg-preview.png)



0 Comments